Waste Management and Sustainable Practices in Urban Environments
Waste management is a critical aspect of urban development and sustainability. As cities continue to grow and populations increase, the generation of waste becomes a significant challenge. Sustainable waste management techniques are essential to minimize environmental impacts, promote resource efficiency, and create a healthier living environment. We are exploring the concept of waste management, sustainable waste management techniques, and the advantages and disadvantages of recycling in the context of building and maintaining sustainable cities.
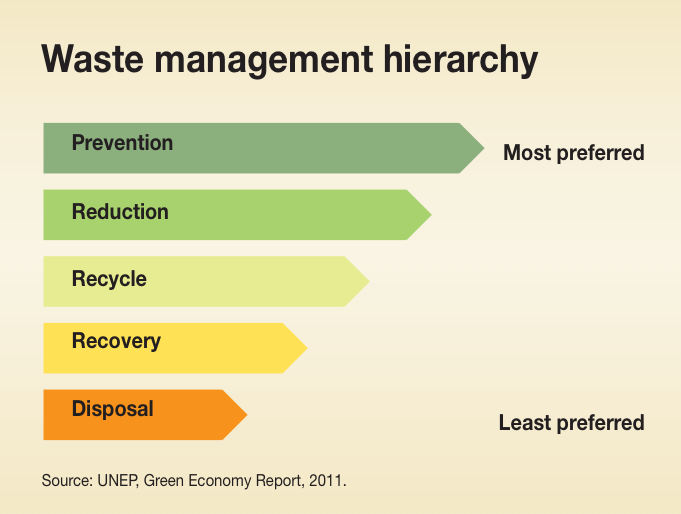
Waste Management Hierarchy
Waste Management
Waste management involves the collection, transportation, processing, recycling, and disposal of waste materials. It is a multifaceted approach that aims to reduce the environmental and health impacts associated with waste generation. The traditional linear model of waste management, which involves the disposal of waste in landfills, is no longer sustainable. Instead, modern waste management strategies focus on a circular economy, emphasizing the reduction, reuse, and recycling of materials.
Sustainable Waste Management Techniques
- 1. Reduce, Reuse, Recycle:
- The three Rs—reduce, reuse, and recycle—form the foundation of sustainable waste management. Reducing waste at the source by minimizing unnecessary packaging and encouraging responsible consumption is the first step. Reusing items, such as containers and packaging, helps extend the life of products. Recycling involves the collection and processing of materials like paper, glass, plastic, and metal to produce new products, reducing the demand for virgin resources.
- 2. Composting:
- Organic waste, such as food scraps and yard waste, can be composted to create nutrient-rich soil amendments. Composting not only diverts organic materials from landfills but also reduces the need for chemical fertilizers in agriculture.
- 3. Waste-to-Energy:
- Waste-to-energy technologies convert non-recyclable waste into energy through processes like incineration or anaerobic digestion. While controversial due to potential environmental and health concerns, when properly regulated, these technologies can contribute to energy production and reduce the volume of waste in landfills.
Advantages of Sustainable Waste Management
- 1. Environmental Benefits:
- Sustainable waste management minimizes environmental pollution, conserves natural resources, and mitigates the release of greenhouse gases. Recycling materials reduces the need for raw material extraction and energy-intensive manufacturing processes, leading to a lower carbon footprint.
- 2. Economic Opportunities:
- The recycling industry creates jobs and economic opportunities. By developing a circular economy, cities can stimulate innovation and entrepreneurship in waste management technologies, fostering a more sustainable and resilient urban economy.
- 3. Health and Well-being:
- Effective waste management contributes to improved public health by reducing the risk of water and air pollution. Proper waste disposal and recycling practices prevent the spread of diseases and create cleaner, healthier living spaces.
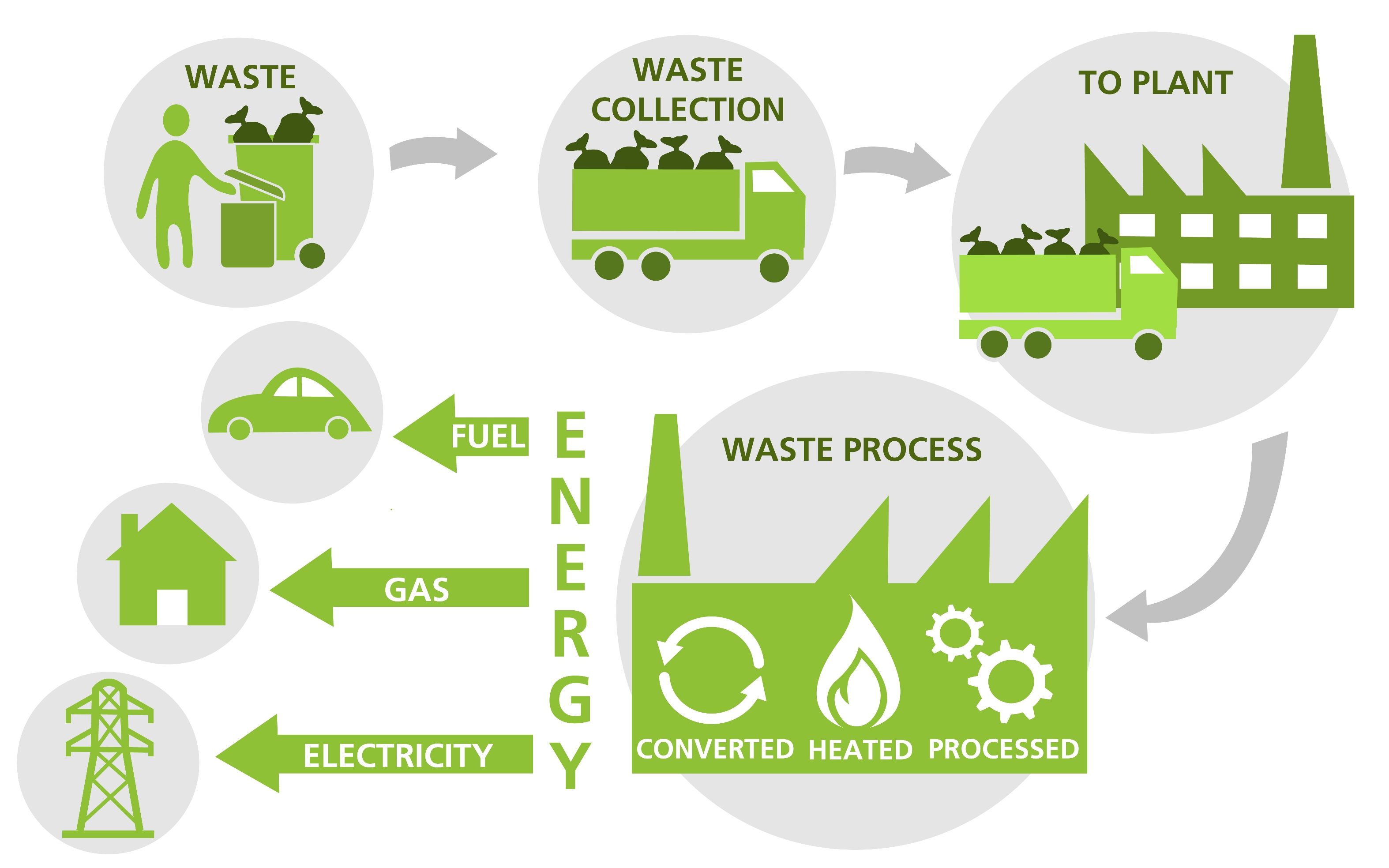
Waste Management Process
Disadvantages of Sustainable Waste Management
- 1. Initial Costs:
- Implementing sustainable waste management practices may involve significant upfront costs for infrastructure development, such as recycling facilities and waste-to-energy plants. However, these costs are often outweighed by long-term benefits.
- 2. Technological Challenges:
- TCertain waste-to-energy technologies, if not properly managed, can release pollutants into the air and pose health risks. Additionally, advancements in recycling technologies are necessary to handle complex materials effectively.
- 3. Behavioral Changes:
- Achieving successful waste management requires changes in consumer behavior, which can be challenging to implement. Public awareness and education campaigns are essential to promote responsible waste disposal and recycling habits.
- 4. Enhanced Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services:
- By preserving natural ecosystems, green architecture promotes biodiversity and contributes to the provision of essential ecosystem services. This includes improved air and water quality, pollination of plants, and the overall health of surrounding ecosystems.
- 5. Increased Property Value:
- Green buildings are often more attractive to environmentally conscious individuals and businesses. As a result, they tend to have higher property values and can command premium rents or prices in the real estate market.
- 6. Regulatory and Certification Incentives:
- Many governments and organizations offer incentives and certifications for green buildings. These may include tax benefits, grants, and recognition for achieving certain environmental standards. These incentives encourage the widespread adoption of sustainable building practices.
In building sustainable cities, waste management plays a pivotal role in mitigating environmental impacts, promoting economic growth, and ensuring public health. Embracing the principles of reduce, reuse, and recycle, along with incorporating innovative technologies, can pave the way for a more sustainable urban future. While challenges exist, the advantages of sustainable waste management far outweigh the disadvantages, making it a critical aspect of building resilient and environmentally conscious cities.